The Indus River Valley civilization, a cradle of human ingenuity and one of the earliest urban civilizations, stands as a testament to the remarkable achievements of ancient societies. This article delves into the indus river valley ap human geography definition, exploring its geographical setting, major characteristics, and the vibrant tapestry of its society, culture, and economy.
Unveiling the Indus River Valley: A Thriving Civilization in the Heart of South Asia
Indus River Valley Civilization Definition: Indus River Valley Ap Human Geography Definition

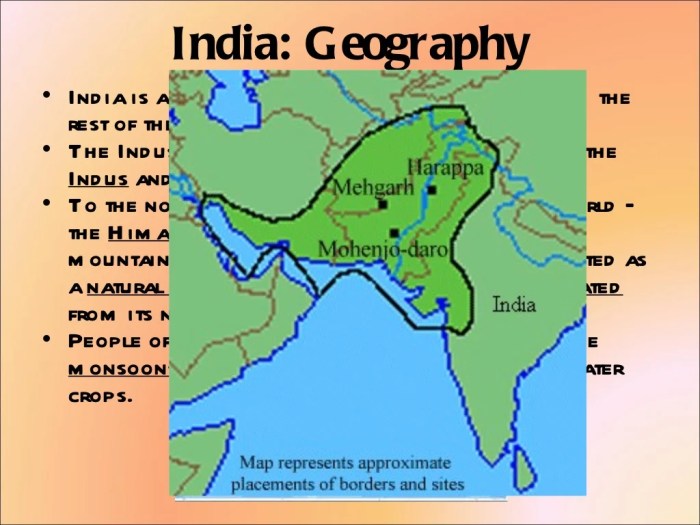
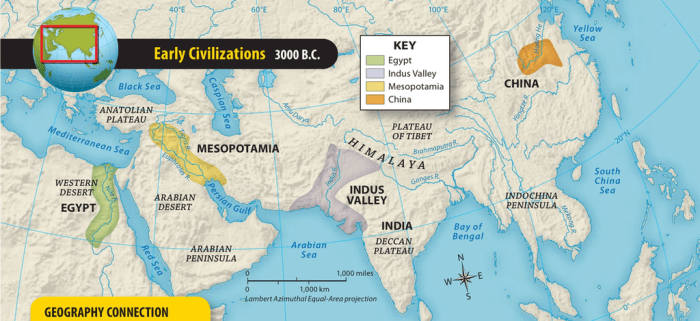
The Indus River Valley Civilization, also known as the Harappan Civilization, flourished in the basins of the Indus River and its tributaries in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent from around 2600 to 1900 BCE.
Major characteristics that define the Indus River Valley Civilization include its highly developed urban centers, sophisticated drainage and sanitation systems, standardized weights and measures, and distinctive pottery and seals.
Indus River Valley society was hierarchical, with a complex social structure and specialized craftspeople. They had a written language, but it has yet to be deciphered.
Indus River Valley Civilization Environment
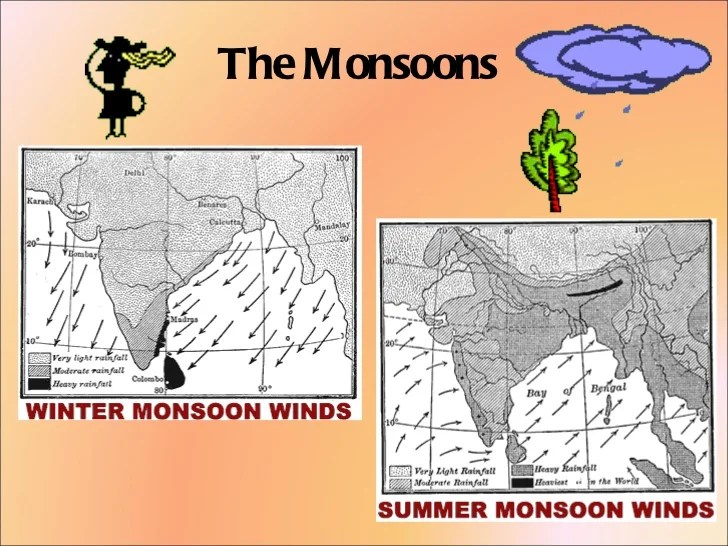
The Indus River Valley is located in a semi-arid region with a hot, dry climate. The vegetation is mostly scrubland and grassland, with some forests in the foothills of the Himalayas.
The Indus River and its tributaries provided the civilization with a reliable source of water for irrigation and transportation.
The environment also posed challenges, such as flooding and drought. The Indus River Valley Civilization developed sophisticated irrigation systems and flood control measures to mitigate these challenges.
Indus River Valley Civilization Cities
The Indus River Valley Civilization is known for its well-planned cities, such as Harappa and Mohenjo-daro.
These cities were laid out in a grid pattern, with streets and houses arranged in blocks. They had public baths, granaries, and other public buildings.
The cities of the Indus River Valley Civilization were among the first in the world to have urban planning and sanitation systems.
Indus River Valley Civilization Culture
The Indus River Valley Civilization had a rich and diverse culture.
Their religious beliefs and practices are not fully understood, but they appear to have worshipped a mother goddess and a bull.
Indus River Valley art and crafts include pottery, jewelry, and sculpture. Their pottery is particularly distinctive, with its black-on-red designs.
Indus River Valley society was hierarchical, with a complex social structure and specialized craftspeople.
Indus River Valley Civilization Economy
The Indus River Valley Civilization was primarily an agricultural society.
They cultivated a variety of crops, including wheat, barley, and cotton.
They also had a thriving trade network, with goods being traded with Mesopotamia and other regions.
Indus River Valley technology and innovation included the development of standardized weights and measures, as well as the use of bronze and copper.
Indus River Valley Civilization Decline, Indus river valley ap human geography definition
The Indus River Valley Civilization declined around 1900 BCE.
The reasons for the decline are not fully understood, but they may have included climate change, deforestation, and invasion.
The decline of the Indus River Valley Civilization had a significant impact on later civilizations in the region.
Top FAQs
What is the geographical extent of the Indus River Valley civilization?
The Indus River Valley civilization flourished in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, encompassing present-day Pakistan and parts of northwestern India.
What are the key characteristics of the Indus River Valley civilization?
The Indus River Valley civilization is renowned for its advanced urban planning, sophisticated drainage and sanitation systems, standardized weights and measures, and a written script that remains undeciphered.
What were the major cities of the Indus River Valley civilization?
The two most prominent cities of the Indus River Valley civilization are Harappa and Mohenjo-daro, both of which showcase remarkable urban planning and architectural sophistication.