Activity 1.1 3 gears vex answers – Embark on an enlightening journey into Vex Activity 1.1 3 Gears Answers, where the intricate world of gears unfolds. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamentals of gears, their significance in Vex robots, and the practical application of these concepts in robotics projects.
Through a captivating narrative and authoritative tone, we unravel the secrets of gears, empowering you to harness their potential in your robotic endeavors.
VEX Activity 1.1
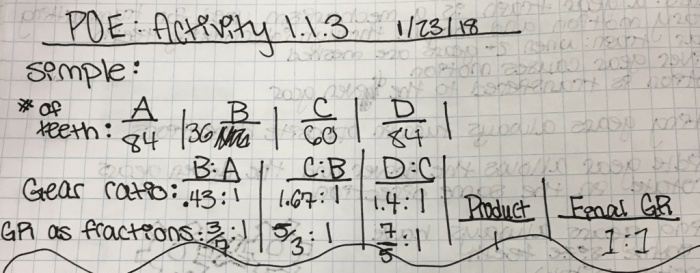
VEX Activity 1.1 introduces students to the basic concepts of engineering design and problem-solving through a hands-on activity. The objective of the activity is to design and build a simple gear train that meets specific requirements.
To complete the activity, students will need the following materials:
- VEX EDR components (gears, shafts, spacers, etc.)
- Screwdriver
- Wrench
- Measuring tape or ruler
Steps to Complete the Activity
1. Students will begin by designing their gear train on paper. They will need to consider the following factors:
- The gear ratio they want to achieve
- The size and type of gears they will need
- The layout of the gear train
2. Once they have designed their gear train on paper, students will begin building it using the VEX EDR components. They will need to use the screwdriver and wrench to assemble the gears, shafts, and spacers.
3. Once the gear train is assembled, students will test it to see if it meets the requirements. They will need to measure the gear ratio and make sure that the gear train runs smoothly.
4. If the gear train does not meet the requirements, students will need to redesign and rebuild it.
Gears and Mechanisms

Gears are mechanical devices that transmit motion and power between rotating shafts. In VEX robots, gears are used to change the speed, torque, and direction of rotation.
There are several different types of gears used in VEX, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common types of gears are:
- Spur gearsare the simplest type of gear. They have straight teeth that mesh with each other. Spur gears are efficient and easy to manufacture, but they can only be used to transmit motion between parallel shafts.
- Helical gearshave teeth that are cut at an angle to the face of the gear. This allows them to transmit motion between shafts that are not parallel. Helical gears are more efficient than spur gears, but they are also more difficult to manufacture.
- Bevel gearshave teeth that are cut on a cone-shaped surface. This allows them to transmit motion between shafts that are perpendicular to each other. Bevel gears are less efficient than spur gears, but they are the only type of gear that can be used to transmit motion between shafts that are not parallel.
- Worm gearshave a worm-shaped gear that meshes with a gear with teeth. Worm gears are very efficient and can transmit a lot of torque, but they are also very slow.
Gears are used in a variety of applications in VEX robots. Some of the most common applications include:
- Drivetrains: Gears are used to transmit power from the motors to the wheels.
- Manipulators: Gears are used to move the arms and claws of manipulators.
- Lifts: Gears are used to raise and lower lifts.
- Indexing mechanisms: Gears are used to index objects, such as balls or cones.
Design and Construction
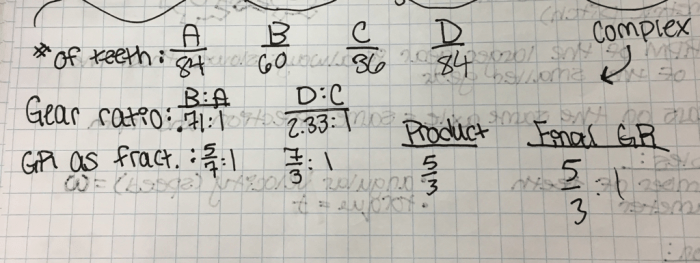
When designing a VEX robot using 3 gears, several key considerations must be taken into account. First, the gear ratio must be carefully selected to achieve the desired speed and torque output. Second, the gears must be properly aligned and meshed to ensure smooth and efficient operation.
Third, the gears must be made of a durable material that can withstand the rigors of competition.
Here are some tips and best practices for constructing a VEX robot with gears:
- Use a gear ratio calculator to determine the ideal gear ratio for your robot.
- Use a gear alignment tool to ensure that the gears are properly aligned.
- Use a gear puller to remove gears from shafts without damaging them.
- Use a thread locker to prevent gears from coming loose.
Here are some examples of successful VEX robot designs that utilize gears:
- The 2018 VEX World Championship-winning robot used a 3-gear drivetrain to achieve a high top speed and acceleration.
- The 2019 VEX World Championship-winning robot used a 3-gear intake system to quickly and efficiently collect game objects.
- The 2020 VEX World Championship-winning robot used a 3-gear elevator system to lift game objects to a high height.
Troubleshooting: Activity 1.1 3 Gears Vex Answers

Identifying and resolving gear-related issues is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of VEX robots. Common problems include gear skipping, excessive noise, and premature wear. Understanding the causes and implementing troubleshooting steps can minimize downtime and improve robot reliability.
Identifying Common Problems
- Gear Skipping:Occurs when gears lose engagement, resulting in power loss and potential damage. Causes include misalignment, excessive backlash, or worn teeth.
- Excessive Noise:Gears may produce excessive noise due to misalignment, improper lubrication, or damaged teeth.
- Premature Wear:Gears can wear prematurely due to excessive loads, insufficient lubrication, or improper material selection.
Troubleshooting Steps, Activity 1.1 3 gears vex answers
- Inspect Gears:Check for damaged teeth, excessive backlash, or misalignment. Replace or adjust gears as necessary.
- Lubricate Gears:Apply a thin layer of appropriate lubricant to reduce friction and wear.
- Adjust Gear Mesh:Ensure proper mesh between gears by adjusting their spacing or using shims.
- Check Load Requirements:Verify that gears are rated for the applied loads to prevent premature wear.
Preventing Gear Problems
- Proper Design:Select gears with appropriate tooth profiles, materials, and sizes for the specific application.
- Careful Assembly:Ensure precise alignment and proper mesh during assembly to minimize stress and wear.
- Regular Maintenance:Inspect gears regularly for wear or damage. Lubricate and adjust gears as needed to extend their lifespan.
Extensions and Applications

VEX Activity 1.1 provides a solid foundation for understanding the principles of gears and mechanisms. To enhance this knowledge, explore extensions that delve into more complex concepts and real-world applications.
By utilizing different gear ratios, you can experiment with the relationship between gear sizes and their impact on speed and torque. Incorporating sensors into the system enables you to gather data and control the mechanism based on external stimuli.
Practical Applications
The concepts learned in VEX Activity 1.1 are fundamental to various robotics projects. For instance, understanding gear ratios is crucial for designing efficient drivetrains, while knowledge of mechanisms is essential for creating functional robotic arms and manipulators.
Real-World Examples
Gears are ubiquitous in robotics. In industrial settings, they are used in conveyors, automated assembly lines, and robotic welding systems. In healthcare, surgical robots utilize gears for precise movements during minimally invasive procedures.
Clarifying Questions
What is the purpose of Vex Activity 1.1?
Vex Activity 1.1 introduces students to the concept of gears and their application in robotics. It provides a hands-on experience in designing, building, and testing a Vex robot that utilizes gears.
What types of gears are used in Vex robots?
Vex robots commonly employ spur gears, bevel gears, and worm gears. Each type serves a specific purpose based on the desired gear ratio and power transmission requirements.
How can I troubleshoot gear-related problems in Vex robots?
Common gear problems include gear skipping, binding, and noise. Troubleshooting involves checking for proper gear alignment, lubrication, and wear. Adjustments or replacements may be necessary to resolve the issue.
